Why Gums Inflamed After Flossing? Relief Tips
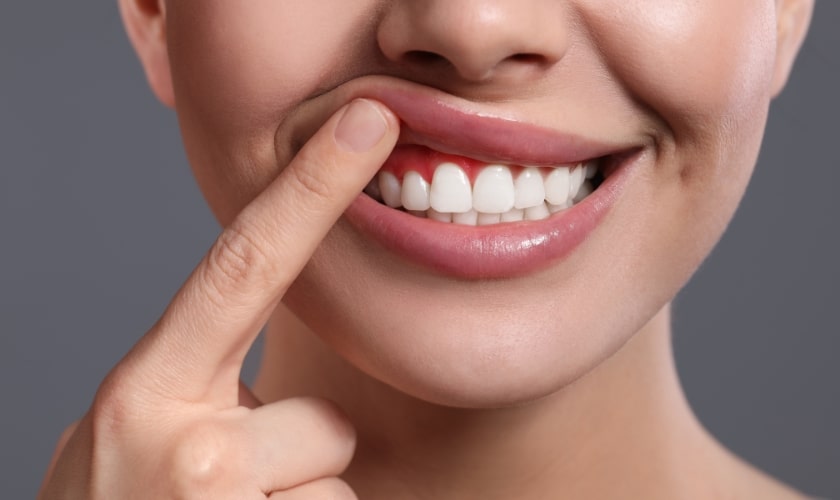

Inflammation of the gums, also known as gingivitis, is a common issue that many people face, and it can be particularly noticeable after flossing. While flossing is an essential part of oral hygiene, it can sometimes cause gum inflammation, especially if you’re new to the practice or haven’t flossed in a while. In this article, we’ll delve into the reasons behind gum inflammation after flossing and provide you with some valuable relief tips to help you overcome this issue.
Understanding Gum Inflammation
Gum inflammation, or gingivitis, occurs when the gums become red, swollen, and tender. This condition is often caused by poor oral hygiene, which allows plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—to build up on the teeth. When plaque is not removed regularly, it can cause irritation and infection of the gums, leading to inflammation. Flossing is a crucial step in removing plaque from between the teeth and under the gumline, where a toothbrush may not reach.
Why Do Gums Become Inflamed After Flossing?
There are several reasons why your gums might become inflamed after flossing:
Introduction of Bacteria: If you haven’t flossed in a while, introducing flossing into your routine can stir up bacteria that have been accumulating under the gumline. This sudden introduction of bacteria can cause an inflammatory response.
Gentleness of Flossing Technique: If you’re flossing too aggressively, you might be causing micro-tears in the gum tissue, which can lead to inflammation.
Pre-existing Gingivitis: If you already have some level of gingivitis, flossing can temporarily exacerbate the condition by disturbing the plaque and bacteria that have formed.
Sensitivity or Allergies: Some individuals might be sensitive to certain materials in dental floss or may have an allergy, though this is rare.
Relief Tips for Inflamed Gums After Flossing
Fortunately, there are several steps you can take to relieve and prevent gum inflammation after flossing:
1. Improve Your Flossing Technique
- Gentle Curving: Curve the floss around the base of each tooth in a “C” shape, making sure to go beneath the gumline but being gentle to avoid damaging the gums.
- Slide, Don’t Snap: Gently slide the floss up and down against the tooth, rather than snapping or forcing it, which can cause micro-tears.
2. Regular Flossing
- Regular flossing helps reduce plaque buildup and prevents the sudden introduction of bacteria that can cause inflammation. Try to floss at least once a day.
3. Use of Interdental Brushes
- For spaces that are too tight for regular floss, consider using interdental brushes. These can be gentler on the gums and more effective for removing plaque from tight spaces.
4. Mouthwash
- Using an antibacterial mouthwash can help reduce bacteria and plaque, thereby reducing inflammation. Look for a mouthwash that carries the American Dental Association (ADA) Seal of Acceptance.
5. Professional Dental Cleaning
- Regular dental cleanings can help remove tartar (hardened plaque) and reduce inflammation. Your dentist can also provide personalized advice on flossing technique and oral hygiene.
6. Maintain Good Oral Hygiene
- besides flossing, ensure you brush your teeth at least twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste and visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings.
Prevention and Long-Term Care
Preventing gum inflammation involves consistent oral hygiene practices, including daily flossing, brushing, and regular dental visits. Over time, your gums should become less inflamed after flossing as they become healthier. Remember, it’s normal for gums to be slightly tender when you first start flossing, especially if you haven’t done it in a while, but this tenderness should decrease with regular practice.
FAQ Section
What is the best flossing technique to avoid gum inflammation?
+The best technique involves gently curving the floss around the base of each tooth in a "C" shape and sliding it up and down against the tooth, rather than snapping or forcing it. This gentle approach helps prevent micro-tears in the gum tissue.
How often should I floss to prevent gum inflammation?
+Flossing once a day is recommended. Regular flossing helps reduce plaque buildup and prevents the sudden introduction of bacteria that can cause inflammation.
Can mouthwash help reduce gum inflammation after flossing?
+Yes, using an antibacterial mouthwash can help reduce bacteria and plaque, thereby reducing inflammation. Look for a mouthwash that carries the American Dental Association (ADA) Seal of Acceptance.
How can I know if my gum inflammation is severe and requires professional help?
+If your gum inflammation persists, worsens, or is accompanied by other symptoms like bleeding gums, bad breath, or loose teeth, it may be a sign of a more severe condition that requires professional dental care. Regular dental check-ups can help identify and manage such conditions early on.
Can gum inflammation after flossing be a sign of an underlying condition?
+Yes, persistent or severe gum inflammation can be a sign of an underlying condition such as gingivitis or periodontitis. It's essential to maintain good oral hygiene practices and consult with a dental professional if you notice any unusual symptoms or if the inflammation doesn't improve with regular flossing and brushing.
Conclusion
Gum inflammation after flossing is a common issue, but with the right techniques, relief tips, and understanding of its causes, you can reduce discomfort and prevent future occurrences. Remember, maintaining good oral hygiene, including regular flossing, brushing, and dental check-ups, is key to preventing and managing gum inflammation. If you’re concerned about your gum health or experience persistent inflammation, it’s always best to consult with a dental professional for personalized advice and care.