What Causes Intravascular Hemolysis? Expert Answers

Intravascular hemolysis, a condition characterized by the premature destruction of red blood cells within the blood vessels, is a complex and potentially life-threatening disorder. To understand the causes of this condition, it’s essential to delve into the underlying mechanisms and risk factors that contribute to its development.
One of the primary causes of intravascular hemolysis is the presence of antibodies against red blood cell antigens. This can occur in conditions such as autoimmune hemolytic anemia, where the immune system mistakenly targets and destroys the body’s own red blood cells. The binding of these antibodies to red blood cells marks them for destruction, which can then occur within the blood vessels, leading to the release of hemoglobin and other cellular contents into the bloodstream.
Another significant cause of intravascular hemolysis is the mechanical damage to red blood cells. This can occur in conditions such as microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, where the small blood vessels are damaged, leading to the mechanical fragmentation of red blood cells as they pass through these narrowed vessels. Similarly, the use of mechanical heart valves or other prosthetic devices can also cause mechanical damage to red blood cells, leading to their premature destruction.
Infections, particularly those caused by certain bacteria, viruses, and parasites, can also trigger intravascular hemolysis. For example, infections with Clostridium perfringens can produce a toxin that directly damages red blood cells, leading to their rapid destruction within the blood vessels. Similarly, malaria, caused by Plasmodium species, can lead to intravascular hemolysis due to the parasite’s invasion and destruction of red blood cells.
Additionally, certain drugs and toxins can cause intravascular hemolysis. For instance, the use of certain antibiotics, such as penicillin, can induce the formation of antibodies against red blood cells in some individuals, leading to their destruction. Similarly, exposure to toxins such as snake venom or certain chemicals can directly damage red blood cells, resulting in their premature destruction.
Nutritional deficiencies, particularly a lack of folate or vitamin B12, can also contribute to intravascular hemolysis. These deficiencies can lead to the production of abnormal red blood cells that are more susceptible to destruction within the blood vessels.
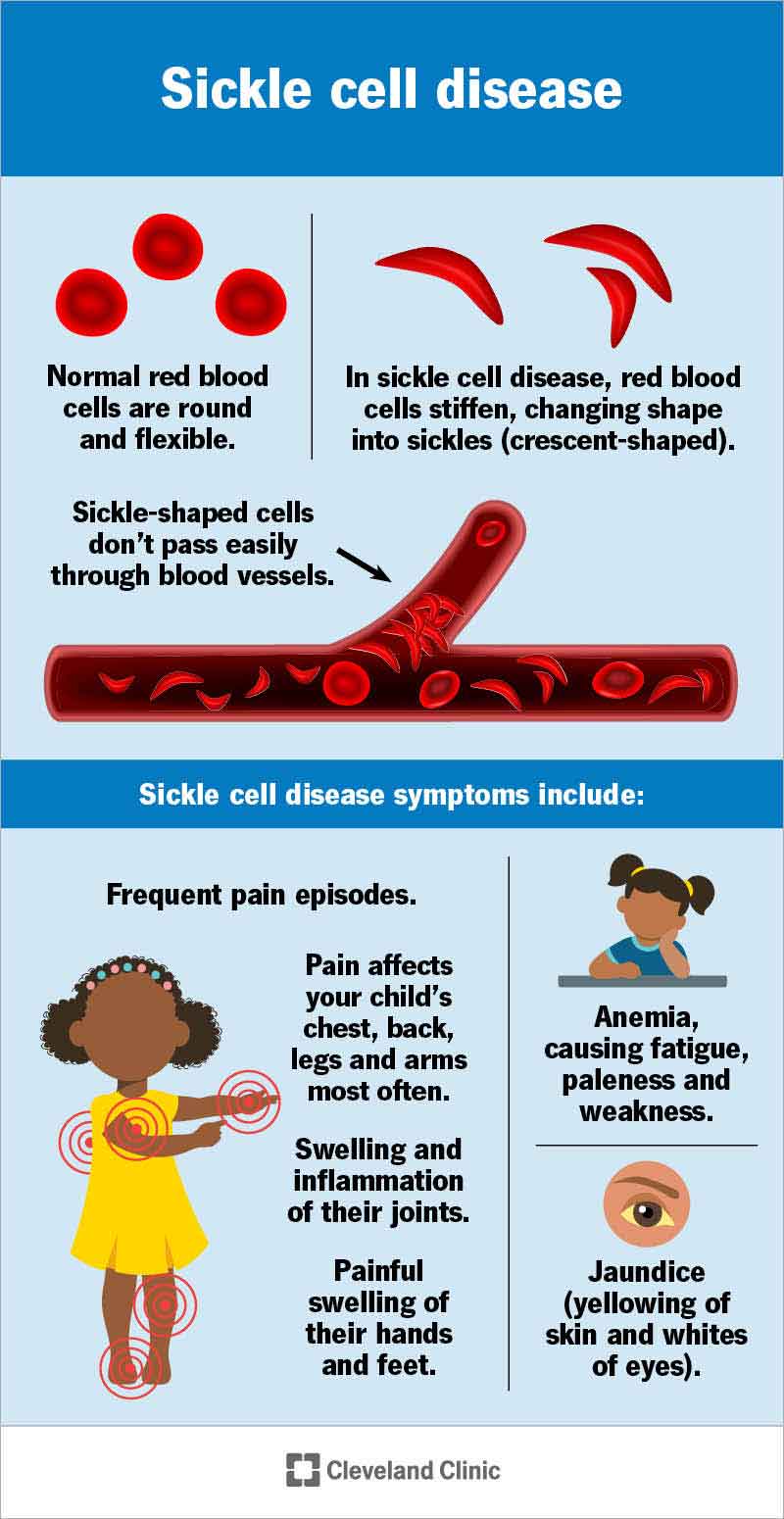
In some cases, intravascular hemolysis can be caused by genetic disorders that affect the structure or function of red blood cells. For example, conditions such as sickle cell disease or hereditary spherocytosis can lead to the production of abnormal red blood cells that are more prone to destruction within the blood vessels.
Understanding the causes of intravascular hemolysis is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies. By identifying the underlying mechanisms and risk factors contributing to this condition, healthcare providers can implement targeted therapies to reduce the destruction of red blood cells and prevent the complications associated with intravascular hemolysis.
In conclusion, intravascular hemolysis is a complex condition with multiple causes and risk factors. By understanding the underlying mechanisms contributing to this disorder, healthcare providers can develop effective treatment strategies to reduce the destruction of red blood cells and improve patient outcomes.
What are the common symptoms of intravascular hemolysis?
+The common symptoms of intravascular hemolysis include jaundice, fatigue, shortness of breath, and dark urine. In severe cases, it can lead to more serious complications such as kidney failure, respiratory distress, and even death.
How is intravascular hemolysis diagnosed?
+Intravascular hemolysis is diagnosed through a combination of laboratory tests, including complete blood counts, reticulocyte counts, and tests for hemolysis such as lactate dehydrogenase and bilirubin levels. Additionally, tests for antibodies against red blood cells and other underlying conditions may be necessary to determine the cause of the hemolysis.
What are the treatment options for intravascular hemolysis?
+Treatment options for intravascular hemolysis depend on the underlying cause and may include corticosteroids, immunosuppressive agents, and other medications to reduce the immune system's attack on red blood cells. In some cases, transfusion of red blood cells or other blood components may be necessary to support the patient's hematologic needs.
The management of intravascular hemolysis requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the underlying causes and risk factors contributing to this condition. By understanding the complex mechanisms involved in intravascular hemolysis, healthcare providers can develop effective treatment strategies to reduce the destruction of red blood cells and improve patient outcomes.
Step-by-Step Approach to Managing Intravascular Hemolysis:

- Identify the underlying cause of the intravascular hemolysis through laboratory tests and other diagnostic procedures.
- Develop a treatment plan that addresses the underlying cause and reduces the immune system's attack on red blood cells.
- Monitor the patient's condition closely and adjust the treatment plan as necessary to ensure optimal outcomes.
- Provide supportive care, including transfusion of red blood cells or other blood components, to support the patient's hematologic needs.
- Follow up with the patient regularly to monitor their condition and adjust the treatment plan as necessary.
Intravascular hemolysis is a complex and potentially life-threatening condition that requires a comprehensive and multidisciplinary approach to management. By understanding the underlying causes and risk factors contributing to this condition, healthcare providers can develop effective treatment strategies to reduce the destruction of red blood cells and improve patient outcomes.
It’s crucial to recognize the significance of early detection and intervention in managing intravascular hemolysis. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of complications. Therefore, it’s essential for healthcare providers to be aware of the signs and symptoms of intravascular hemolysis and to have a comprehensive approach to its management.
The key takeaway from this discussion is that intravascular hemolysis is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive and multidisciplinary approach to management. By understanding the underlying causes and risk factors contributing to this condition, healthcare providers can develop effective treatment strategies to reduce the destruction of red blood cells and improve patient outcomes.
In conclusion, intravascular hemolysis is a complex and potentially life-threatening condition that requires a comprehensive and multidisciplinary approach to management. By understanding the underlying causes and risk factors contributing to this condition, healthcare providers can develop effective treatment strategies to reduce the destruction of red blood cells and improve patient outcomes.
The importance of ongoing research and education in the field of intravascular hemolysis cannot be overstated. As our understanding of this condition evolves, so too will our approaches to its management. It’s essential for healthcare providers to stay up-to-date with the latest developments and advancements in the field to ensure that patients receive the best possible care.
Pros and Cons of Different Treatment Approaches for Intravascular Hemolysis:

| Treatment Approach | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Corticosteroids | Effective in reducing inflammation and immune system activity | Can have significant side effects, including weight gain and mood changes |
| Immunosuppressive Agents | Effective in reducing the immune system's attack on red blood cells | Can increase the risk of infections and other complications |
| Transfusion of Red Blood Cells | Can provide rapid support for patients with severe anemia | Can carry risks, including transfusion reactions and transmission of infectious diseases |
Ultimately, the management of intravascular hemolysis requires a careful balancing of the pros and cons of different treatment approaches. By considering the unique needs and circumstances of each patient, healthcare providers can develop effective treatment strategies that minimize risks and maximize benefits.
As we continue to advance our understanding of intravascular hemolysis, it’s essential to consider the broader implications of this condition. By recognizing the complex interplay of factors that contribute to intravascular hemolysis, we can develop more effective treatment strategies and improve patient outcomes.
Future Trends in the Management of Intravascular Hemolysis:
The future of intravascular hemolysis management is likely to involve the development of new and innovative treatment approaches. As our understanding of the underlying causes and risk factors contributing to this condition evolves, so too will our approaches to its management. Some potential future trends in the management of intravascular hemolysis include the use of gene therapy, stem cell transplantation, and other novel therapeutic approaches.
In conclusion, intravascular hemolysis is a complex and potentially life-threatening condition that requires a comprehensive and multidisciplinary approach to management. By understanding the underlying causes and risk factors contributing to this condition, healthcare providers can develop effective treatment strategies to reduce the destruction of red blood cells and improve patient outcomes. As we continue to advance our understanding of intravascular hemolysis, it’s essential to consider the broader implications of this condition and to develop new and innovative treatment approaches to improve patient care.