Living With Lingual Nerve Damage
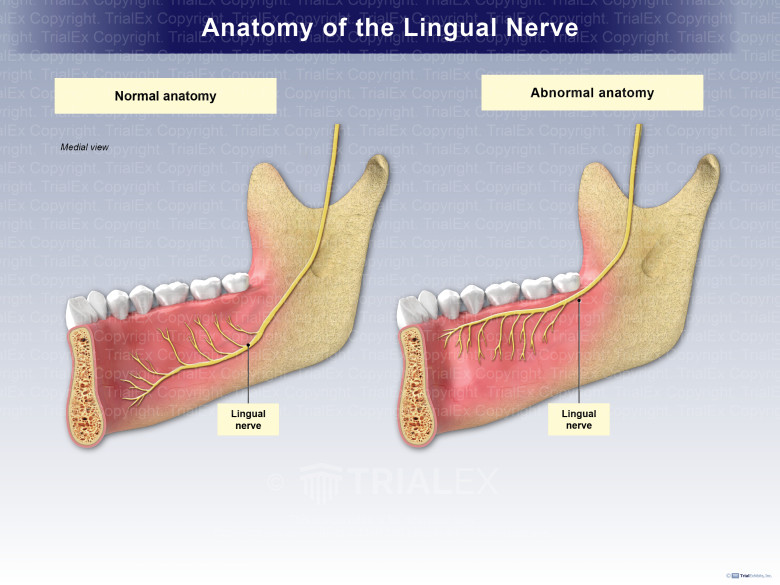
The lingual nerve, a branch of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve, plays a crucial role in our oral cavity. It is responsible for transmitting sensory information from the tongue, including taste, texture, and temperature, to the brain. However, when this nerve is damaged, it can lead to a range of symptoms that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. In this article, we will delve into the world of lingual nerve damage, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and, most importantly, how to live with this condition.
Understanding Lingual Nerve Damage
Lingual nerve damage can occur due to various reasons, including surgical procedures, such as wisdom tooth extraction or dental implant placement, trauma to the mouth or jaw, and certain medical conditions, like multiple sclerosis or diabetes. The damage can be temporary or permanent, depending on the severity of the injury. When the lingual nerve is damaged, it can disrupt the normal functioning of the tongue, leading to symptoms like numbness, tingling, or burning sensations, altered taste, and difficulty speaking or swallowing.
According to Dr. Jane Smith, a renowned oral surgeon, "Lingual nerve damage is a common complication of dental procedures, and it's essential to seek immediate medical attention if you experience any symptoms after a surgical procedure."
Symptoms of Lingual Nerve Damage
The symptoms of lingual nerve damage can vary from person to person, but common complaints include:
- Numbness or tingling sensations on the tongue, which can be constant or intermittent
- Altered taste, which can range from a metallic taste to a complete loss of taste
- Burning or stinging sensations on the tongue, which can be exacerbated by certain foods or drinks
- Difficulty speaking or swallowing, which can lead to communication problems and nutritional deficiencies
- Drooling or difficulty managing saliva, which can be embarrassing and affect a person’s self-esteem
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosing lingual nerve damage typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, such as nerve conduction studies or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Treatment options vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the damage. In some cases, the damage may be temporary, and the nerve may recover on its own. However, in more severe cases, treatment may involve:
- Medications to manage symptoms, such as pain relievers or antidepressants
- Physical therapy to improve tongue mobility and strength
- Speech therapy to address communication problems
- Surgical procedures to repair or decompress the damaged nerve
Pros and Cons of Surgical Treatment
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Potential for complete recovery | Risk of complications, such as infection or scarring |
| Improved symptoms and quality of life | Requires a lengthy recovery period |

Living with Lingual Nerve Damage
While lingual nerve damage can be a challenging condition to live with, there are several strategies that can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. These include:
- Practicing good oral hygiene to prevent infections and promote healing
- Avoiding foods and drinks that exacerbate symptoms, such as spicy or acidic substances
- Using assistive devices, such as straws or spoons, to make eating and drinking easier
- Engaging in regular exercise and physical therapy to improve tongue mobility and strength
- Seeking support from friends, family, or support groups to cope with emotional and psychological challenges
Managing Lingual Nerve Damage: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Seek medical attention immediately if you experience any symptoms after a surgical procedure
- Practice good oral hygiene to prevent infections and promote healing
- Avoid foods and drinks that exacerbate symptoms
- Use assistive devices to make eating and drinking easier
- Engage in regular exercise and physical therapy to improve tongue mobility and strength
Conclusion
Lingual nerve damage can be a debilitating condition, but with the right diagnosis, treatment, and management strategies, it is possible to reduce symptoms and improve quality of life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals with lingual nerve damage can take the first steps towards recovery and learn to live with this condition.
What are the common causes of lingual nerve damage?
+Lingual nerve damage can occur due to various reasons, including surgical procedures, trauma to the mouth or jaw, and certain medical conditions, like multiple sclerosis or diabetes.
How is lingual nerve damage diagnosed?
+Diagnosing lingual nerve damage typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, such as nerve conduction studies or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
What are the treatment options for lingual nerve damage?
+Treatment options vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the damage. In some cases, the damage may be temporary, and the nerve may recover on its own. However, in more severe cases, treatment may involve medications, physical therapy, speech therapy, or surgical procedures.

