Gum Dark Spot
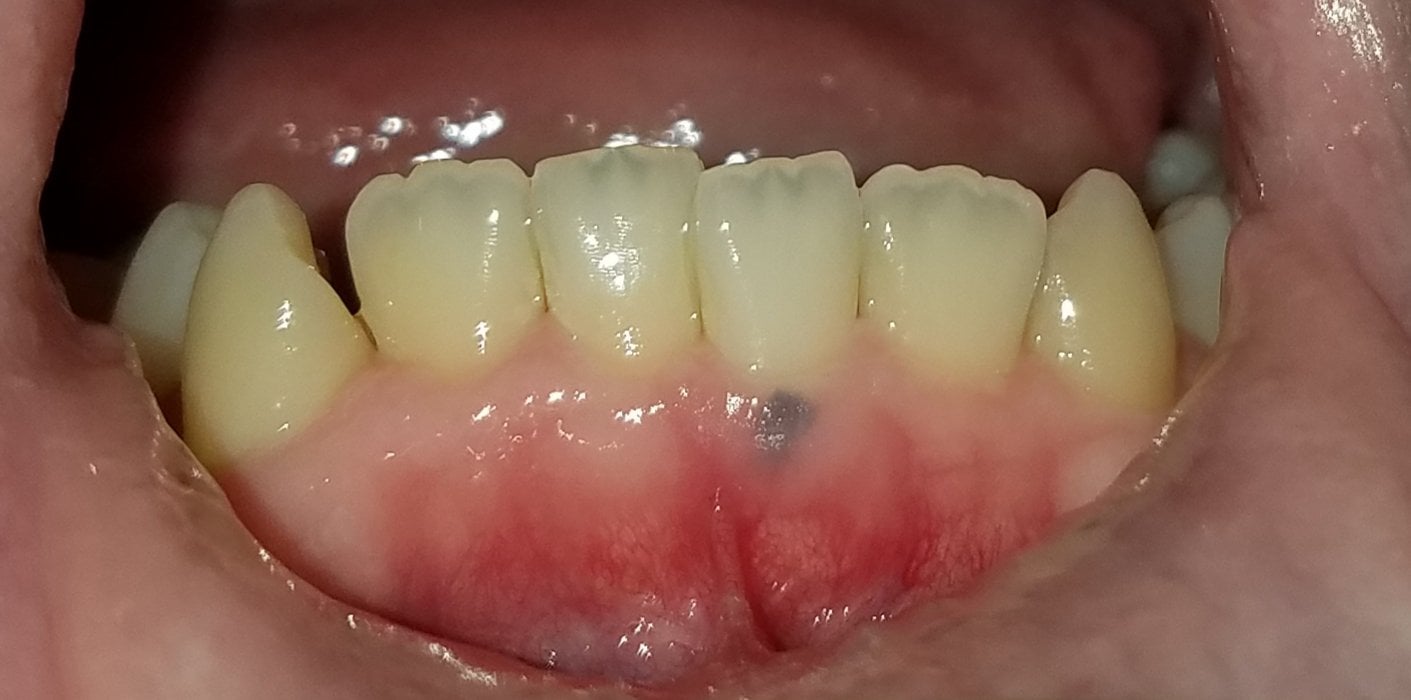
The appearance of dark spots on the gum can be a cause for concern for many individuals. These discolorations, also known as gum melanin deposits or oral melanotic macules, can vary in size, shape, and color, ranging from light brown to deep black. While they are often benign, it’s essential to understand the possible causes, diagnosis, and treatment options to ensure oral health and aesthetics.
One of the primary causes of dark spots on the gum is the accumulation of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin and hair color. This can occur due to various factors, including:
- Hormonal changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels, such as those experienced during pregnancy or menopause, can stimulate melanin production, leading to the formation of dark spots.
- Injury or trauma: Physical trauma to the gum, such as a bite or a cut, can cause inflammation and subsequent melanin deposition.
- Smoking and tobacco use: The chemicals present in tobacco products can irritate the gum, leading to the formation of dark spots.
- Medication side effects: Certain medications, such as antimalarials and minocycline, can cause oral pigmentation as a side effect.
- Systemic diseases: Conditions like Addison’s disease, Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, and neurofibromatosis can lead to oral melanin deposits.
In some cases, dark spots on the gum can be a sign of a more serious underlying condition, such as:
- Oral cancer: Although rare, oral cancer can manifest as a dark spot or lesion on the gum.
- Melanoma: A type of skin cancer that can occur in the mouth, including the gum.
To diagnose the cause of dark spots on the gum, a dentist or oral pathologist will typically perform a visual examination, review the patient’s medical history, and may conduct diagnostic tests, such as:
- Biopsy: A tissue sample is taken from the affected area and examined under a microscope to rule out cancer or other conditions.
- Imaging studies: X-rays or other imaging tests may be used to evaluate the extent of the discoloration and rule out underlying structural issues.
Treatment options for dark spots on the gum depend on the underlying cause and may include:
- Monitoring: If the dark spot is deemed benign, the dentist may recommend regular monitoring to ensure it does not change or grow.
- Laser treatment: Laser therapy can be used to remove or lighten the dark spot.
- Surgical excision: In some cases, surgical removal of the affected tissue may be necessary.
- Topical treatments: Creams or gels containing ingredients like hydrogen peroxide or vitamin C can help lighten the discoloration.
It’s essential to note that prevention is key. Maintaining good oral hygiene, avoiding tobacco products, and protecting the mouth from injury can help reduce the risk of developing dark spots on the gum.
In conclusion, dark spots on the gum can be caused by a range of factors, from harmless melanin deposits to more serious underlying conditions. By staying informed and seeking professional advice, individuals can ensure their oral health and aesthetics are protected.
What are the most common causes of dark spots on the gum?
+The most common causes of dark spots on the gum include hormonal changes, injury or trauma, smoking and tobacco use, medication side effects, and systemic diseases.
Can dark spots on the gum be a sign of oral cancer?
+Although rare, oral cancer can manifest as a dark spot or lesion on the gum. It's essential to consult a dentist or oral pathologist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
What are the treatment options for dark spots on the gum?
+Treatment options for dark spots on the gum depend on the underlying cause and may include monitoring, laser treatment, surgical excision, and topical treatments.
By prioritizing oral health and seeking professional advice, individuals can address dark spots on the gum and maintain a healthy, beautiful smile.