Gum Bump Guide: Diagnosis And Treatment Options

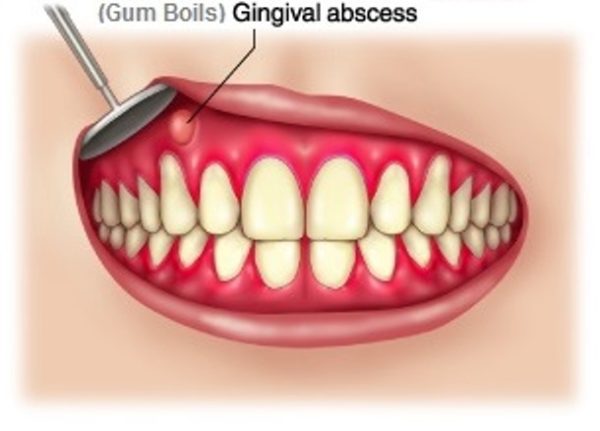
The appearance of a gum bump can be a cause for concern, as it may indicate an underlying issue with oral health. These bumps, also known as gum boils or parulis, can be painful and may interfere with daily activities such as eating and speaking. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the diagnosis and treatment options for gum bumps, providing valuable insights and expert advice to help individuals navigate this common oral health issue.
Understanding Gum Bumps: Causes and Symptoms
Gum bumps can be caused by a variety of factors, including poor oral hygiene, gum disease, and trapped food particles. They can also be a symptom of an underlying condition such as a dental abscess or cyst. The symptoms of a gum bump may include:
- A visible bump or swelling on the gum tissue
- Pain or tenderness in the affected area
- Redness or inflammation of the surrounding gum tissue
- Pus or discharge from the bump
- Bad breath or a foul taste in the mouth
Diagnosis: How to Identify a Gum Bump
Diagnosing a gum bump typically involves a visual examination of the affected area, as well as a review of the individual’s medical and dental history. Your dentist may use a variety of diagnostic tools, including:
- Visual examination: Your dentist will visually examine the affected area to look for signs of inflammation, redness, or swelling.
- X-rays: Your dentist may take X-rays of the affected area to determine if there are any underlying issues, such as a dental abscess or cyst.
- Periodontal probing: Your dentist may use a periodontal probe to measure the depth of the gum pocket and determine if there is any bone loss.
| Diagnostic Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Visual Examination | Visual examination of the affected area to look for signs of inflammation, redness, or swelling. |
| X-rays | X-rays of the affected area to determine if there are any underlying issues, such as a dental abscess or cyst. |
| Periodontal Probing | Periodontal probing to measure the depth of the gum pocket and determine if there is any bone loss. |
Treatment Options: What to Expect
The treatment for a gum bump will depend on the underlying cause. In some cases, a gum bump may resolve on its own with improved oral hygiene and self-care. However, in other cases, more invasive treatment may be necessary. Some common treatment options for gum bumps include:
- Antibiotics: If the gum bump is caused by a bacterial infection, your dentist may prescribe antibiotics to help clear up the infection.
- Drainage: If the gum bump is caused by a dental abscess or cyst, your dentist may need to drain the abscess or cyst to relieve pressure and promote healing.
- Surgical removal: In some cases, surgical removal of the gum bump may be necessary to remove the affected tissue and promote healing.
Treatment Steps
- Antibiotics: If the gum bump is caused by a bacterial infection, your dentist may prescribe antibiotics to help clear up the infection.
- Drainage: If the gum bump is caused by a dental abscess or cyst, your dentist may need to drain the abscess or cyst to relieve pressure and promote healing.
- Surgical removal: In some cases, surgical removal of the gum bump may be necessary to remove the affected tissue and promote healing.
Prevention: Tips for Maintaining Good Oral Health
Preventing gum bumps and maintaining good oral health requires a combination of good oral hygiene habits and regular dental check-ups. Here are some tips to help you keep your teeth and gums healthy:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste
- Floss daily to remove food particles and plaque from between your teeth
- Use an antibacterial mouthwash to help kill bacteria and reduce inflammation
- Avoid smoking and tobacco products, which can increase your risk of gum disease
- Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings
Pros and Cons of Treatment Options
- Antibiotics: Effective in treating bacterial infections, but may have side effects such as diarrhea and stomach upset.
- Drainage: Can provide quick relief from pain and pressure, but may require multiple visits to the dentist.
- Surgical removal: Can provide a permanent solution, but may require anesthesia and can be more expensive.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes a gum bump?
+A gum bump can be caused by a variety of factors, including poor oral hygiene, gum disease, and trapped food particles. It can also be a symptom of an underlying condition such as a dental abscess or cyst.
How do I diagnose a gum bump?
+Diagnosing a gum bump typically involves a visual examination of the affected area, as well as a review of the individual's medical and dental history. Your dentist may use a variety of diagnostic tools, including X-rays and periodontal probing.
What are the treatment options for a gum bump?
+The treatment for a gum bump will depend on the underlying cause. In some cases, a gum bump may resolve on its own with improved oral hygiene and self-care. However, in other cases, more invasive treatment may be necessary, such as antibiotics, drainage, or surgical removal.
In conclusion, gum bumps can be a cause for concern, but with proper diagnosis and treatment, they can be effectively managed. By understanding the causes and symptoms of gum bumps, individuals can take steps to prevent them and maintain good oral health. Remember to always visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings, and don’t hesitate to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms of a gum bump.


