Female Vs Male Bone: Know The Key Differences

The human skeleton is a complex and fascinating system, comprising 206 bones that provide structure, support, and protection to the body. While the basic structure of the skeletal system is the same in both males and females, there are several key differences between female and male bones. These differences are primarily driven by reproductive and hormonal factors, as well as adaptations for childbearing and other physiological processes.
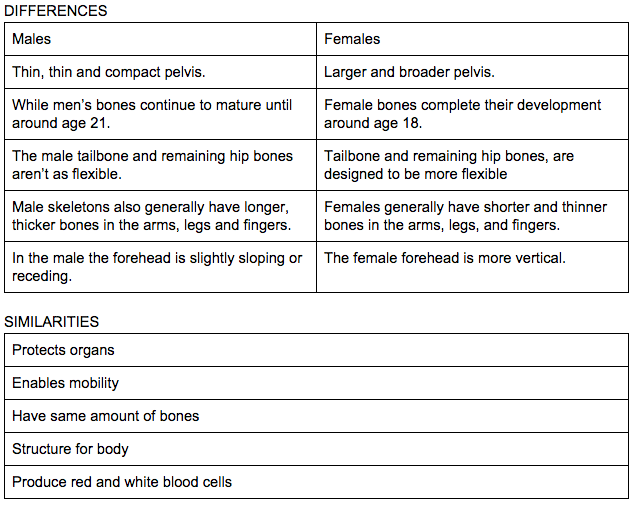
One of the most significant differences between female and male bones is the pelvis. The female pelvis is wider and shallower than the male pelvis, with a larger outlet to facilitate childbirth. This is because the female pelvis needs to accommodate the passage of a baby’s head during delivery, which requires a wider birth canal. In contrast, the male pelvis is narrower and deeper, with a smaller outlet. This difference in pelvis shape and size is one of the most distinctive characteristics of the female and male skeletons.
Another key difference between female and male bones is the density and strength of the bones. Generally, male bones are denser and stronger than female bones, particularly in the hips, legs, and upper body. This is due to the higher levels of testosterone in males, which stimulates bone growth and density. Female bones, on the other hand, are more prone to osteoporosis, particularly after menopause, due to the decline in estrogen levels. Estrogen helps to maintain bone density, and its loss can lead to a decrease in bone mass and strength.
The bones of the upper body also differ between females and males. The male skeleton tends to have broader shoulders and a larger chest cavity than the female skeleton, which allows for greater muscle mass and strength. The female skeleton, on the other hand, has a narrower shoulder and a smaller chest cavity, which is adapted for childbearing and breastfeeding. The female ribs are also more flexible than the male ribs, allowing for greater expansion of the chest during pregnancy and childbirth.
In addition to these differences, there are also variations in the size and shape of the long bones, such as the femur (thigh bone) and the humerus (upper arm bone). Male long bones tend to be longer and thicker than female long bones, which can affect the overall height and proportions of the body. For example, the average length of the femur in an adult male is approximately 48 cm (19 in), while in an adult female it is approximately 45 cm (18 in).
The hands and feet also exhibit sex differences in the bones. The male hands and feet tend to be larger and more robust than the female hands and feet, with thicker bones and a more pronounced arch in the foot. The female hands and feet, on the other hand, are generally smaller and more delicate, with thinner bones and a less pronounced arch.
The differences between female and male bones have important implications for various fields, including medicine, anthropology, and forensic science. For example, in forensic anthropology, the analysis of skeletal remains can help determine the sex of an individual, which is critical for identifying human remains and solving crimes. In medicine, understanding the differences between female and male bones can inform the diagnosis and treatment of bone-related disorders, such as osteoporosis and fractures.
In conclusion, the bones of females and males exhibit distinct differences in shape, size, and density, driven by reproductive and hormonal factors, as well as adaptations for childbearing and other physiological processes. These differences are essential for understanding human anatomy and have significant implications for various fields of study.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between the female and male pelvis?
+The main difference between the female and male pelvis is the width and depth. The female pelvis is wider and shallower, with a larger outlet to facilitate childbirth, while the male pelvis is narrower and deeper.
Why are male bones generally denser and stronger than female bones?
+Male bones are generally denser and stronger than female bones due to the higher levels of testosterone in males, which stimulates bone growth and density.
What is the difference between the female and male long bones?
+Male long bones tend to be longer and thicker than female long bones, which can affect the overall height and proportions of the body.
Why are the hands and feet of males generally larger and more robust than those of females?
+The hands and feet of males tend to be larger and more robust than those of females due to the higher levels of testosterone, which stimulates bone growth and density.
What are the implications of the differences between female and male bones for various fields of study?
+The differences between female and male bones have important implications for various fields, including medicine, anthropology, and forensic science. Understanding these differences can inform the diagnosis and treatment of bone-related disorders, as well as the analysis of skeletal remains in forensic anthropology.
In the context of human evolution, the differences between female and male bones can provide valuable insights into the selective pressures that have shaped the human skeleton over time. For example, the wider pelvis in females is thought to have evolved to accommodate the larger brain size of human infants, which requires a larger birth canal. Similarly, the stronger bones in males may have evolved to support the demands of hunting and other physically demanding activities.
Key Differences Between Female and Male Bones: A Summary

- The female pelvis is wider and shallower than the male pelvis, with a larger outlet to facilitate childbirth.
- Male bones are generally denser and stronger than female bones, particularly in the hips, legs, and upper body.
- The female skeleton has a narrower shoulder and a smaller chest cavity than the male skeleton, which is adapted for childbearing and breastfeeding.
- Males tend to have broader shoulders and a larger chest cavity than females, allowing for greater muscle mass and strength.
- The hands and feet of males tend to be larger and more robust than those of females, with thicker bones and a more pronounced arch in the foot.
Overall, the differences between female and male bones are a fascinating aspect of human anatomy, with significant implications for our understanding of human evolution, physiology, and health. By exploring these differences in more depth, we can gain a greater appreciation for the complexity and diversity of the human body, as well as the many factors that shape our skeletal system.


