Childs Teeth Xray Guide
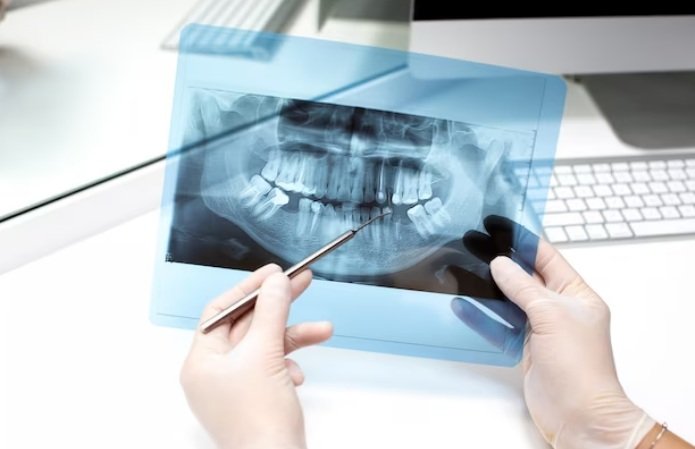
The use of X-rays in pediatric dentistry has become a crucial tool for diagnosing and treating dental issues in children. Dental X-rays, also known as radiographs, provide valuable information about the health of a child’s teeth and surrounding tissues. As a parent, it’s natural to have questions and concerns about the use of X-rays on your child’s teeth. This comprehensive guide aims to provide you with a thorough understanding of the importance of X-rays in pediatric dentistry, the different types of X-rays used, and what to expect during an X-ray examination.
Why Are X-Rays Necessary for Children’s Teeth?
X-rays are an essential diagnostic tool in pediatric dentistry, allowing dentists to detect oral health issues that may not be visible during a visual examination. Some of the reasons why X-rays are necessary for children’s teeth include:
- Detecting Tooth Decay: X-rays help dentists identify tooth decay, even in its early stages, when it’s not visible to the naked eye. This allows for early treatment and prevents the decay from progressing.
- Monitoring Tooth Development: X-rays help track the development of teeth, including the formation of new teeth and the presence of any abnormalities.
- Identifying Orthodontic Issues: X-rays can reveal issues with tooth alignment and bite, allowing for early intervention and orthodontic treatment.
- Detecting Dental Abscesses: X-rays can help identify dental abscesses, which are painful infections that can spread to other parts of the face and skull if left untreated.
Types of X-Rays Used in Pediatric Dentistry
There are several types of X-rays used in pediatric dentistry, each with its own unique benefits and uses. Some of the most common types of X-rays include:
- Intraoral X-Rays: These X-rays are taken inside the mouth and provide detailed images of individual teeth and surrounding tissues.
- Extraoral X-Rays: These X-rays are taken outside the mouth and provide a broader view of the teeth and jawbone.
- Panoramic X-Rays: These X-rays provide a wide view of the upper and lower jaw, including the teeth, jawbone, and surrounding tissues.
- Cephalometric X-Rays: These X-rays provide a detailed view of the skull and facial structure, helping dentists diagnose issues with tooth alignment and bite.
What to Expect During an X-Ray Examination
If your child needs an X-ray examination, here’s what you can expect:
- Preparation: Your child will be asked to remove any jewelry or metal objects that may interfere with the X-ray.
- Positioning: Your child will be positioned in a chair or on a table, depending on the type of X-ray being taken.
- X-Ray Machine: The X-ray machine will be placed near your child’s mouth, and the X-ray will be taken.
- Film or Digital Sensor: A film or digital sensor will be placed in your child’s mouth to capture the X-ray image.
- Results: The X-ray images will be reviewed by the dentist, who will discuss the results with you and recommend any necessary treatment.
It's essential to note that X-rays are a safe and essential diagnostic tool in pediatric dentistry. The amount of radiation used in dental X-rays is very small, and the benefits of X-rays far outweigh the risks.
Safety Concerns and Radiation Exposure
As a parent, it’s natural to have concerns about the safety of X-rays and radiation exposure. Here are some facts to put your mind at ease:
- Low Radiation Levels: Dental X-rays use very low levels of radiation, significantly lower than other medical X-rays.
- Thyroid Collar: A thyroid collar is used to protect the thyroid gland from radiation.
- Lead Apron: A lead apron is used to protect the body from radiation.
- Digital X-Rays: Digital X-rays use less radiation than traditional film X-rays.
Practical Application Guide: Preparing Your Child for an X-Ray Examination
To ensure a smooth and successful X-ray examination, follow these practical tips:
- Explain the Procedure: Explain the X-ray procedure to your child in a way they can understand, to reduce anxiety and fear.
- Choose a Pediatric Dentist: Choose a pediatric dentist who has experience working with children and uses the latest X-ray technology.
- Follow Instructions: Follow the instructions provided by the dentist or X-ray technician to ensure the X-ray is taken correctly.
- Be Present: Be present during the X-ray examination to provide support and comfort to your child.
- Arrive early to complete any necessary paperwork and prepare your child for the X-ray examination.
- Explain the X-ray procedure to your child and answer any questions they may have.
- Choose a pediatric dentist who has experience working with children and uses the latest X-ray technology.
- Follow the instructions provided by the dentist or X-ray technician to ensure the X-ray is taken correctly.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some frequently asked questions about X-rays and children’s teeth:
How often should my child have X-rays?
+The frequency of X-rays depends on your child's oral health and the dentist's recommendations. Typically, children should have X-rays every 6-12 months.
Are X-rays safe for my child?
+Yes, X-rays are safe for children. The amount of radiation used in dental X-rays is very small, and the benefits of X-rays far outweigh the risks.
Can I be present during the X-ray examination?
+Yes, you can be present during the X-ray examination to provide support and comfort to your child.
In conclusion, X-rays are a valuable diagnostic tool in pediatric dentistry, providing essential information about the health of your child’s teeth and surrounding tissues. By understanding the importance of X-rays, the different types of X-rays used, and what to expect during an X-ray examination, you can make informed decisions about your child’s oral health. Remember to choose a pediatric dentist who has experience working with children and uses the latest X-ray technology, and follow the instructions provided to ensure a smooth and successful X-ray examination.


