Bentall Procedure Cardiac

The Bentall procedure is a complex surgical operation used to treat aortic root aneurysms and other defects of the aortic valve and root. It involves replacing the aortic valve, the aortic root, and the ascending aorta with a composite graft, which includes a mechanical valve and a Dacron tube. This procedure is named after Hugh Bentall, the British cardiac surgeon who first described it in 1968.
Indications for the Bentall Procedure
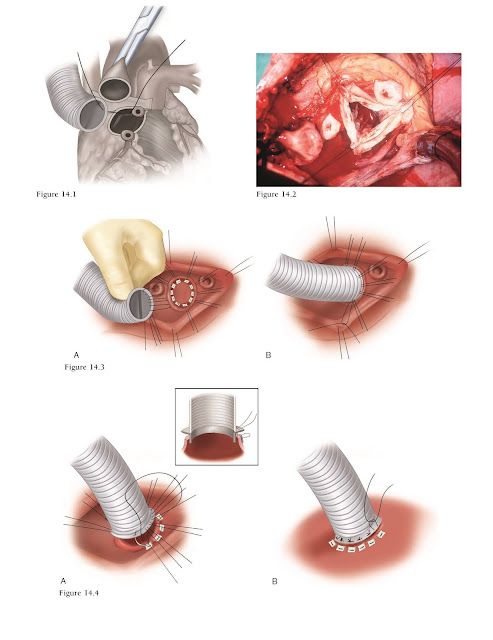
The Bentall procedure is typically indicated for patients with conditions that affect the aortic root, such as:
- Aneurysms of the aortic root or ascending aorta
- Aortic dissection, which is a tear in the inner layer of the aorta
- Marfan syndrome, a genetic disorder that affects the body’s connective tissue and can lead to aortic root aneurysms
- Other conditions that cause aortic root dilation or aneurysm, such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome or Turner syndrome
Preoperative Evaluation
Before undergoing the Bentall procedure, patients typically undergo a comprehensive preoperative evaluation, which includes:
- Echocardiography to assess the function of the aortic valve and the size of the aortic root
- Computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans to evaluate the size and location of the aneurysm or dissection
- Coronary angiography to assess the coronary arteries for any blockages or other abnormalities
- Blood tests to evaluate the patient’s overall health and to check for any signs of infection or inflammation
Surgical Technique

The Bentall procedure is a complex and technically demanding operation that requires a high level of expertise and experience. The surgery is typically performed through a median sternotomy, which involves making an incision in the center of the chest to access the heart and aorta.
- Cardiopulmonary Bypass: The first step in the Bentall procedure is to establish cardiopulmonary bypass, which involves diverting the patient’s blood flow away from the heart and lungs and into a heart-lung machine. This allows the surgical team to operate on a still heart.
- Aortic Cross-Clamping: Once cardiopulmonary bypass is established, the surgeon clamps the aorta to prevent blood from flowing into the aortic root and to allow for a bloodless field.
- Aortic Root Replacement: The surgeon then removes the diseased aortic root and valve and replaces it with a composite graft, which includes a mechanical valve and a Dacron tube.
- Coronary Artery Reimplantation: The coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart muscle, are then reimplanted into the composite graft.
- Aortic Anastomosis: The descending aorta is then anastomosed (connected) to the composite graft, and the aortic cross-clamp is removed.
Postoperative Care
After the Bentall procedure, patients typically require close monitoring and care in the intensive care unit (ICU) for several days. This includes:
- Mechanical Ventilation: Patients are typically placed on mechanical ventilation to support their breathing and to help them recover from the anesthesia.
- Inotropic Support: Patients may require inotropic support, such as medications to help the heart pump more effectively.
- Antibiotic Prophylaxis: Patients typically receive antibiotic prophylaxis to prevent infection.
- Pain Management: Patients require effective pain management to help them recover from the surgery and to prevent discomfort.
Complications and Risks
The Bentall procedure is a complex and high-risk operation, and patients should be aware of the potential complications and risks, which include:
- Mortality: The mortality rate for the Bentall procedure is around 5-10%, although this can vary depending on the individual patient’s condition and the surgeon’s experience.
- Stroke: Patients are at risk of stroke during the procedure, which can occur due to emboli (clots) or other factors.
- Myocardial Infarction: Patients are at risk of myocardial infarction (heart attack) during the procedure, which can occur due to the stress of surgery on the heart.
- Renal Failure: Patients are at risk of renal failure, which can occur due to the use of cardiopulmonary bypass and other factors.
- Infection: Patients are at risk of infection, which can occur due to the use of prosthetic materials and other factors.
Long-Term Results

The long-term results of the Bentall procedure are generally excellent, with most patients experiencing significant improvement in their symptoms and quality of life. However, patients require lifelong follow-up and monitoring to prevent complications and to ensure the longevity of the prosthetic valve and graft.
Follow-Up Care
Patients who undergo the Bentall procedure require regular follow-up care, which includes:
- Echocardiography: Regular echocardiography to assess the function of the prosthetic valve and the size of the aortic root.
- CT or MRI Scans: Regular CT or MRI scans to evaluate the size and location of the aneurysm or dissection.
- Blood Tests: Regular blood tests to evaluate the patient’s overall health and to check for any signs of infection or inflammation.
- Medications: Patients typically require lifelong anticoagulation therapy to prevent thromboembolism (blood clots) and other complications.
FAQ Section
What is the Bentall procedure?
+The Bentall procedure is a complex surgical operation used to treat aortic root aneurysms and other defects of the aortic valve and root.
What are the indications for the Bentall procedure?
+The Bentall procedure is typically indicated for patients with conditions that affect the aortic root, such as aneurysms, dissections, and Marfan syndrome.
What are the risks and complications of the Bentall procedure?
+The Bentall procedure is a complex and high-risk operation, and patients should be aware of the potential complications and risks, which include mortality, stroke, myocardial infarction, renal failure, and infection.
What is the long-term outcome of the Bentall procedure?
+The long-term results of the Bentall procedure are generally excellent, with most patients experiencing significant improvement in their symptoms and quality of life.
What kind of follow-up care is required after the Bentall procedure?
+Patients who undergo the Bentall procedure require regular follow-up care, which includes echocardiography, CT or MRI scans, blood tests, and medications to prevent complications and to ensure the longevity of the prosthetic valve and graft.


