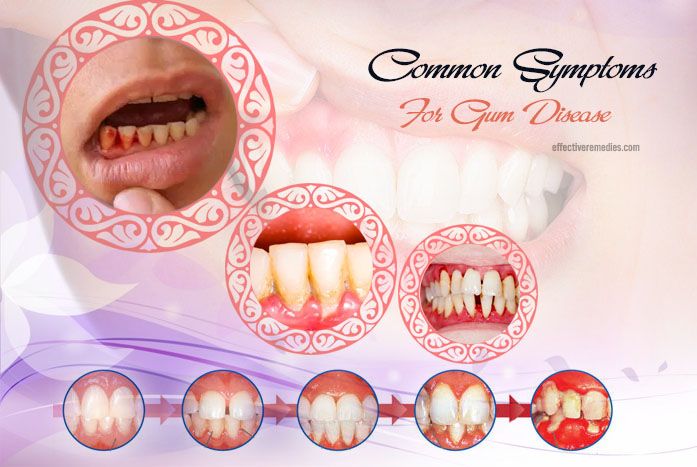
12+ Xray Secrets For Identifying Tooth Decay Early
Tooth decay, a condition characterized by the destruction of tooth enamel, is a prevalent issue affecting dental health worldwide. Early identification of tooth decay is crucial for effective management and prevention of further complications. Dental X-rays have become an indispensable tool in dentistry for detecting tooth decay in its early stages, among other dental issues. Here, we will delve into the secrets of using X-ray technology for the early identification of tooth decay, discussing the benefits, techniques, and interpretations of dental X-rays in this context.
Understanding Tooth Decay
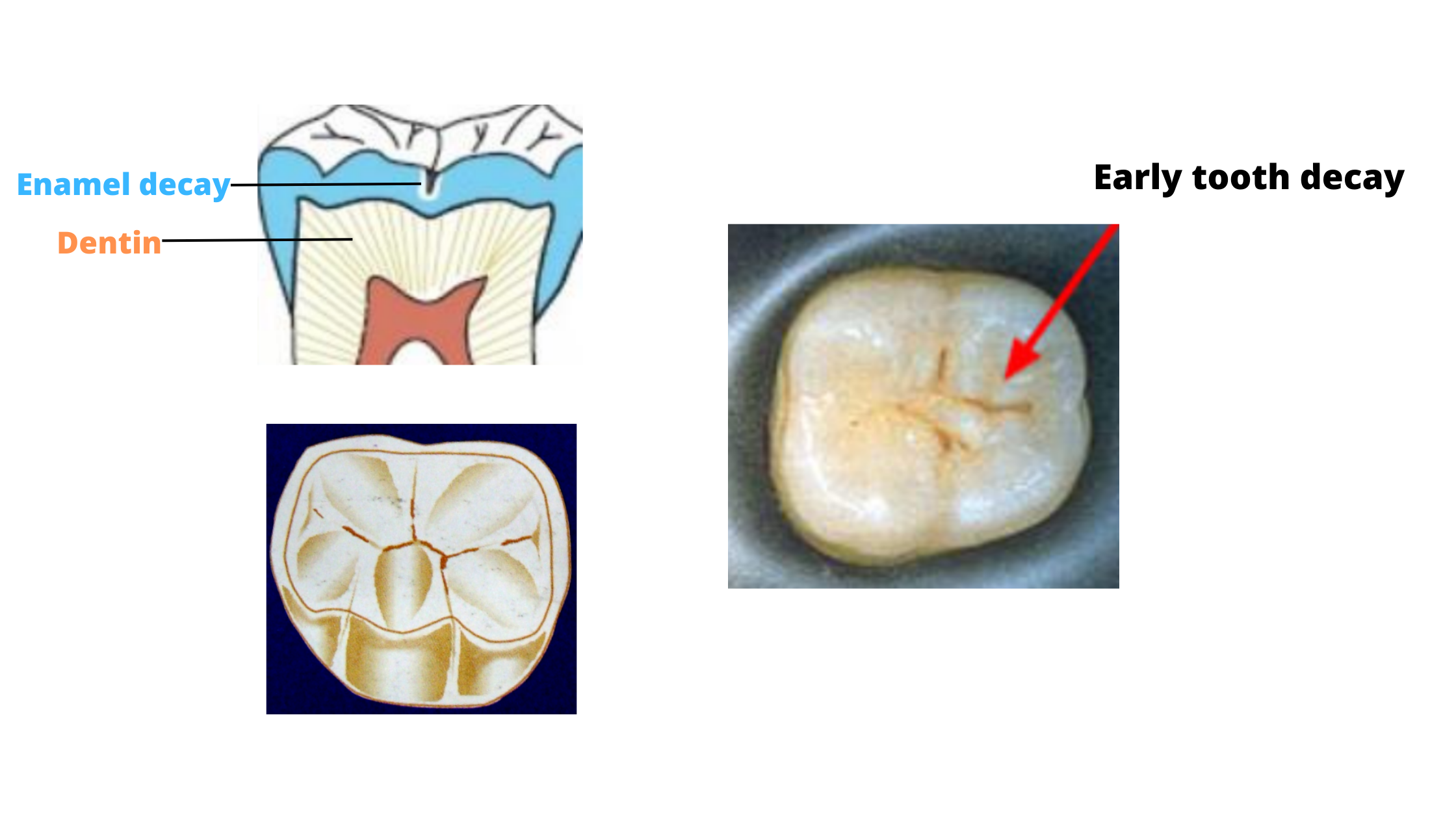
Before diving into the specifics of X-ray diagnostics, it’s essential to understand what tooth decay is. Tooth decay, also known as dental caries, occurs when bacteria in the mouth break down food, particularly sugars and carbohydrates, and produce acid. This acid can damage the enamel of the tooth, leading to a cavity. If left untreated, the decay can progress through the enamel and into the softer dentin beneath, potentially reaching the pulp and causing more severe issues like abscesses or requiring root canal treatments.
The Role of X-rays in Dentistry
X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation that can penetrate solid objects, including teeth and bones, to varying degrees. In dentistry, X-rays are used for diagnostic purposes, allowing dentists to visualize the internal structure of teeth and surrounding tissues. They are particularly useful for detecting issues that are not visible during a regular dental examination, such as cavities between teeth, the extent of decay, bone loss around teeth due to periodontal disease, and the position of unerupted teeth.
Secrets for Identifying Tooth Decay Early with X-rays
Frequency of X-rays: Regular X-rays are crucial for early detection of tooth decay. The frequency at which X-rays should be taken depends on the individual’s oral health status and risk factors for decay. High-risk patients may require X-rays more frequently, such as every six to twelve months, while low-risk patients might only need them every two to three years.
Types of X-ray Views: Different types of X-ray views provide unique insights into dental health. Bite-wing X-rays are excellent for detecting interproximal caries (cavities between teeth), while periapical X-rays show the entire tooth, from the crown to the root, and are useful for assessing the tooth’s pulp and surrounding bone.
Digital X-rays: The shift to digital X-ray technology has improved the ability to detect tooth decay early. Digital X-rays reduce radiation exposure, provide instant images, and can be enhanced for better visualization of dental structures.
Bitewing X-rays for Interproximal Decay: These X-rays are particularly effective for identifying decay between teeth, which can be difficult to detect visually. By showing the upper and lower teeth biting down on the X-ray film, bitewing X-rays can reveal even the earliest signs of interproximal caries.
Panoramic X-rays for Overall Assessment: While panoramic X-rays provide a wide view of the upper and lower jaw in a single image, they are less detailed than intraoral X-rays. However, they can be useful for detecting issues such as impacted teeth, cysts, and tumors, and for planning extensive restorative or surgical procedures.
CAD/CAM Technology: The integration of computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) technology in dentistry allows for precise restorations that can help prevent future decay by ensuring a tight, well-sealed fit of fillings and crowns.
Monitoring Changes Over Time: Regular comparison of current X-rays with previous ones can help in detecting subtle changes that may indicate the onset of tooth decay. This comparative analysis is a powerful tool for early detection.
Combining X-rays with Other Diagnostic Tools: X-rays should be used in conjunction with a thorough clinical examination, including visual inspection and probing, for a comprehensive assessment of oral health.
Low Radiation Exposure: Modern dental X-ray machines and digital X-ray systems are designed to minimize radiation exposure, making them safer for patients. This reduction in radiation dose encourages the use of X-rays as a diagnostic tool without undue concern for safety.
TRAINING AND EXPERIENCE: The ability to interpret X-rays accurately for early signs of tooth decay requires training and experience. Dentists must be skilled in reading X-rays and understanding the subtleties that differentiate healthy teeth from those with early decay.
Patient Education: Educating patients about the importance of regular X-rays, good oral hygiene practices, and dietary habits that reduce the risk of tooth decay is crucial. Patients who understand their role in prevention are more likely to adhere to recommendations for X-rays and other preventive measures.
New Technologies and Future Directions: The field of dental diagnostics is evolving, with advances in imaging technologies such as cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) offering three-dimensional views of dental structures. These technologies may enhance the detection and management of tooth decay in the future.
Conclusion
The early identification of tooth decay is critical for maintaining good oral health, preventing the progression of dental caries, and minimizing the need for extensive dental treatments. X-rays, particularly when used in conjunction with other diagnostic tools and preventive dental practices, are a valuable resource in this endeavor. By understanding the benefits, techniques, and interpretations of dental X-rays, individuals can better appreciate the role these images play in their dental care and take proactive steps towards a healthier, cavity-free smile.
FAQ Section
How often should I get dental X-rays to check for tooth decay?
+The frequency of dental X-rays depends on your oral health status and risk factors for decay. Your dentist can advise on the best schedule for you, but it could range from every six months for high-risk patients to every two to three years for low-risk individuals.
Are dental X-rays safe, considering the radiation exposure?
+Modern dental X-ray technology is designed to minimize radiation exposure. The benefits of early detection of tooth decay and other dental issues far outweigh the minimal risks associated with dental X-rays.
Can dental X-rays detect issues other than tooth decay?
+Yes, dental X-rays can detect a variety of dental issues, including bone loss around teeth due to periodontal disease, the position of unerupted teeth, abscesses, and cysts. They provide a comprehensive view of dental health.
Do I need X-rays if I have a dental crown or filling?
+X-rays can still be beneficial even if you have dental restorations. They can help detect decay under existing fillings or crowns, as well as issues with the surrounding teeth or bone structure.
Can children get dental X-rays?
+Yes, children can and should have dental X-rays as part of their regular dental check-ups. The frequency and type of X-ray may vary based on the child’s age, oral health, and risk of dental problems. Pediatric dentists use X-rays to monitor the development of teeth and detect any potential issues early on.
How can I reduce my risk of getting tooth decay?
+To reduce your risk of tooth decay, practice good oral hygiene by brushing your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing once a day, and visiting your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings. Limiting sugary and acidic foods and drinks can also help prevent decay.