12 Thyrotropin Receptor Ab Insights For Better Health
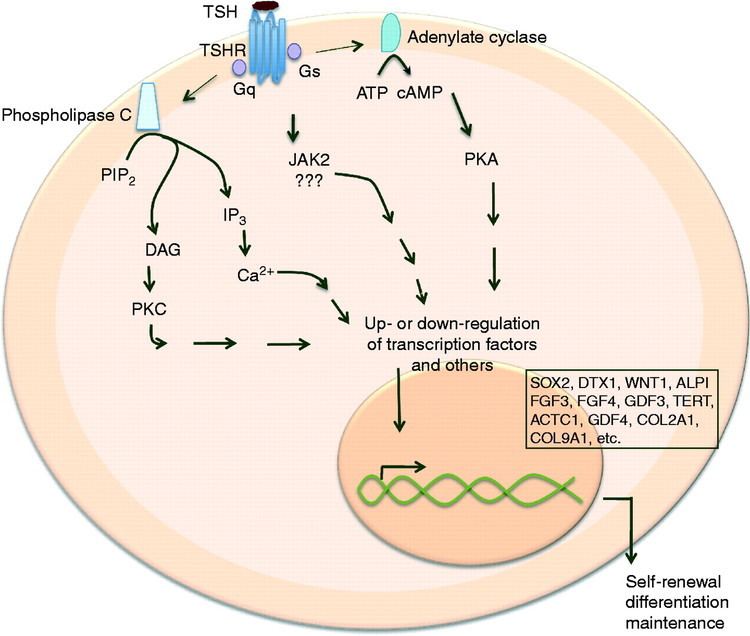
The thyrotropin receptor, also known as the thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor (TSHR), plays a crucial role in regulating thyroid function and overall health. Abnormalities in the TSHR can lead to various thyroid-related disorders, making it essential to understand the intricacies of this receptor. Here, we delve into 12 key insights about thyrotropin receptor antibodies (TRAb) and their implications for better health.
Understanding Thyrotropin Receptor Antibodies (TRAb)

TRAb are autoantibodies that target the TSHR, either stimulating or blocking its activity. These antibodies are a hallmark of autoimmune thyroid diseases, such as Graves’ disease and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Understanding the mechanisms and effects of TRAb is vital for diagnosing and managing thyroid disorders.
TRAb tests are essential for distinguishing between different forms of hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism, allowing for more accurate diagnoses and tailored treatment plans.
1. Graves' Disease and TRAb
In Graves’ disease, TRAb stimulate the TSHR, leading to an overproduction of thyroid hormones (hyperthyroidism). This condition is characterized by symptoms such as weight loss, palpitations, and exophthalmos. Effective management of Graves’ disease often involves reducing TRAb levels or blocking their action on the TSHR.
2. Hashimoto's Thyroiditis and TRAb
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, on the other hand, is associated with blocking TRAb, which can lead to a decrease in thyroid hormone production (hypothyroidism). This condition is marked by symptoms like fatigue, weight gain, and dry skin. Understanding the role of TRAb in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is crucial for developing targeted therapies.
3. Diagnostic Challenges
Diagnosing thyroid disorders based on TRAb levels can be challenging due to the complexity of autoimmune responses and the variability of clinical presentations. A comprehensive approach, including clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and sometimes imaging studies, is necessary for accurate diagnosis.
Step-by-Step Diagnostic Approach:
- Clinical evaluation for symptoms and signs of thyroid disease
- Thyroid function tests (TFTs) to assess hormone levels
- TRAb tests to detect the presence and type of antibodies
- Imaging studies (e.g., thyroid ultrasound) if necessary
4. Treatment Strategies
Treatment for TRAb-related thyroid diseases depends on the underlying condition. For Graves’ disease, options include antithyroid medications, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery. For Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, thyroid hormone replacement therapy is often prescribed.
Antithyroid Medications vs. Radioactive Iodine Therapy:
Pros of Antithyroid Medications: Can be effective in managing symptoms without permanent damage to the thyroid gland.
Cons of Antithyroid Medications: May have side effects and require long-term use.
Pros of Radioactive Iodine Therapy: Can provide a permanent solution by reducing thyroid tissue.
Cons of Radioactive Iodine Therapy: May lead to hypothyroidism requiring lifelong thyroid hormone replacement.
5. Implications for Pregnancy
TRAb can have significant implications for pregnancy, as they can cross the placenta and affect fetal thyroid function. Women with a history of Graves’ disease or Hashimoto’s thyroiditis require close monitoring during pregnancy to manage maternal and fetal health.
6. The Role of Genetics
Genetic factors play a role in the susceptibility to autoimmune thyroid diseases. Understanding the genetic predisposition can help in early detection and preventive measures.
7. Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors, such as iodine intake and exposure to certain pollutants, can trigger or exacerbate autoimmune thyroid diseases. Awareness of these factors can help in prevention and management strategies.
8. Thyroid Hormone Regulation
Thyroid hormones are crucial for metabolic regulation, growth, and development. Understanding how TRAb affect thyroid hormone production and regulation is vital for maintaining health and preventing complications.
9. Autoimmune Thyroiditis
Autoimmune thyroiditis, characterized by inflammation of the thyroid gland due to an autoimmune response, can lead to both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism phases. TRAb play a central role in this condition, making their measurement critical for diagnosis and treatment.
10. TRAb in Thyroid Nodules and Cancer
The presence of TRAb can sometimes be associated with thyroid nodules and cancer, although the relationship is not fully understood. Further research is needed to elucidate the role of TRAb in these conditions.
11. Novel Therapeutic Approaches
Research into novel therapeutic approaches, including immunomodulatory therapies and TRAb-targeting treatments, holds promise for improving the management of autoimmune thyroid diseases.
12. Future Perspectives
As our understanding of TRAb and their role in thyroid health evolves, so too will our diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. Future research directions include personalized medicine approaches, exploring the microbiome’s influence on autoimmune thyroid diseases, and developing more sensitive and specific diagnostic tools.
What is the primary function of the thyrotropin receptor?
+The primary function of the thyrotropin receptor (TSHR) is to regulate thyroid function by responding to thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and stimulating the production of thyroid hormones.
How do thyrotropin receptor antibodies (TRAb) affect thyroid function?
+TRAb can either stimulate or block the TSHR, leading to overproduction (hyperthyroidism) or underproduction (hypothyroidism) of thyroid hormones, respectively.
What are the implications of TRAb for pregnancy?
+TRAb can cross the placenta and affect fetal thyroid function, necessitating close monitoring and management of maternal and fetal health during pregnancy.
In conclusion, understanding thyrotropin receptor antibodies and their role in thyroid health is crucial for the diagnosis, treatment, and management of autoimmune thyroid diseases. By recognizing the complexities of TRAb and their implications for health, we can work towards better prevention, diagnosis, and treatment strategies for these conditions.