10 Arthritis Facts Revealing Deadly Consequences
Arthritis, often perceived as a mere joints issue, encompasses a broad range of conditions that affect not just the joints, but also other tissues and organs in the body. The severity and impact of arthritis can be misunderstood, leading to underestimation of its potential deadly consequences. Here’s a comprehensive exploration of arthritis, breaking down the myths, understanding its types, and delving into the lesser-known but critical aspects of this condition.
Introduction to Arthritis
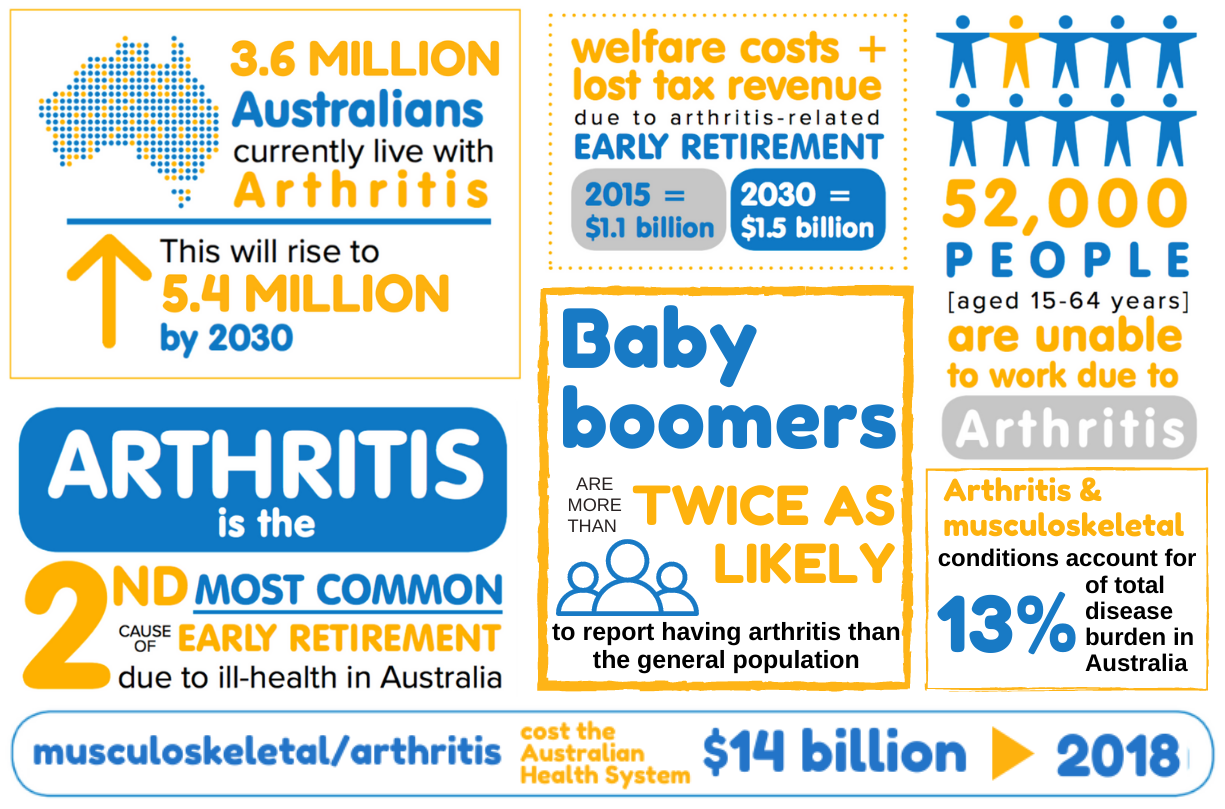
Arthritis is not a single disease; it is an informal way of referring to joint pain or joint disease. There are more than 100 different types of arthritis and related conditions. People of all ages, sexes, and races can and do have arthritis, and it is the leading cause of disability in America. The most common types of arthritis include osteoarthritis (OA), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), fibromyalgia, and gout, each with its unique set of causes, symptoms, and treatments.
Types of Arthritis and Their Impact
Osteoarthritis (OA): The most common type of arthritis, OA is caused by wear and tear on a joint. It can occur in any joint, but it most often affects hands, knees, hips, and spine. While OA is typically associated with aging, it can also result from joint injuries or obesity.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): This is an autoimmune disease that can cause joint pain and damage throughout the body. RA can also affect the tissues and organs in the body, leading to a wide range of symptoms beyond joint pain, including fever, fatigue, and loss of appetite.
Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA): Occurring in some people with psoriasis, PsA can cause joint pain, stiffness, and swelling. Like RA, PsA is an autoimmune disease and can lead to significant joint damage if left untreated.
Deadly Consequences of Untreated Arthritis
While arthritis itself is not typically considered fatal, the complications arising from chronic inflammation, medication side effects, and decreased mobility can indeed have lethal consequences.
Increased Risk of Heart Disease: Chronic inflammation from rheumatoid arthritis and other types can increase the risk of heart disease, which is a leading cause of death worldwide. Studies have shown that individuals with RA are at a higher risk of experiencing a heart attack or stroke compared to those without the disease.
Lymphoma: Certain types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, slightly increase the risk of developing lymphoma, a type of cancer. The chronic inflammation associated with RA may contribute to the development of lymphoma, although the exact mechanisms are not fully understood.
Infections: People with certain types of arthritis may be more susceptible to infections due to a weakened immune system. For example, those with RA may have impaired immune responses, making them more prone to infections like pneumonia.
Mental Health Issues: The chronic pain and disability associated with arthritis can lead to depression and anxiety, which, if severe and untreated, can have fatal outcomes. The emotional toll of living with a chronic condition should not be underestimated, and mental health support is crucial for individuals with arthritis.
Kidney and Liver Damage: Long-term use of certain medications for arthritis, like NSAIDs, can lead to kidney and liver damage. These conditions, if not properly managed, can lead to severe health complications, including organ failure.
Osteoporosis: Certain types of arthritis and the medications used to treat them can increase the risk of osteoporosis, leading to fractures that can be life-threatening, especially in the elderly.
Surgical Complications: In advanced cases, surgery may be necessary. However, as with any surgery, there are risks of complications, some of which can be fatal.
Social Isolation: The pain and decreased mobility associated with arthritis can lead to social isolation, which has been linked to numerous health issues, including a weakened immune system and increased risk of heart disease.
Management and Treatment
While there is no cure for most types of arthritis, there are many effective treatments and management strategies that can help alleviate symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve quality of life. These include:
- Medications: Such as pain relievers, corticosteroids, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
- Physical Therapy: To maintain joint mobility and strengthen the muscles around the joints.
- Lifestyle Changes: Including weight loss, a balanced diet, and regular exercise can reduce the stress on joints and decrease inflammation.
Prognosis and Future Outlook
The outlook for individuals with arthritis has improved significantly with advancements in medical treatment and care. Early diagnosis and appropriate management can prevent or reduce the severity of many complications associated with arthritis. Research continues to uncover new insights into the causes of arthritis and potential new treatments, offering hope for better management and potentially even cures in the future.
Conclusion
Arthritis is more than just a nuisance; it can have serious and potentially deadly consequences if not properly managed. Understanding the different types of arthritis, recognizing its symptoms, and adhering to treatment plans can significantly reduce the risk of complications and improve the quality of life for those affected. By acknowledging the complexity and severity of arthritis, individuals can seek the necessary care and support, ultimately living more fulfilling lives despite their condition.
What are the most common symptoms of arthritis?
+The most common symptoms of arthritis include pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased range of motion in the joints. The severity of these symptoms can vary greatly among different types of arthritis and individuals.
Can arthritis be prevented?
+While some risk factors for arthritis, such as genetics, cannot be changed, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding joint injuries, and not smoking can reduce the risk of developing certain types of arthritis, such as osteoarthritis.
How does diet affect arthritis?
+A balanced diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce inflammation and promote overall health. Certain foods, such as those high in sugar and saturated fats, may exacerbate arthritis symptoms in some individuals.
Can exercise worsen arthritis symptoms?
+While high-impact exercises may exacerbate joint pain in some cases, regular, moderate exercise, such as swimming or cycling, can help reduce stiffness, improve joint mobility, and strengthen the muscles around the joints, ultimately benefiting individuals with arthritis.
Is there a cure for arthritis?
+Currently, there is no cure for most types of arthritis. However, with the right treatment and self-management strategies, it is possible to reduce symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve the quality of life for individuals with arthritis.
How does arthritis affect mental health?
+Arthritis can significantly impact mental health, leading to increased rates of depression and anxiety due to chronic pain, reduced mobility, and the emotional burden of living with a chronic condition. Seeking support from mental health professionals can be beneficial for many individuals with arthritis.